AI Robots Assist Nurses in Combating Burnout and Revolutionizing Hospital Care
Taiwan hospitals deploy Nurabot, an AI nursing robot, to ease nurse shortages and enhance patient care.

The global healthcare sector is bracing for a critical shortfall, with projections estimating a startling shortage of 4.5 million nurses by 2030. Experts have identified burnout as one of the primary factors driving this exodus from the nursing profession. In an effort to preserve patient care standards and support their existing workforce, hospitals in Taiwan are turning to cutting-edge solutions—namely, artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics.
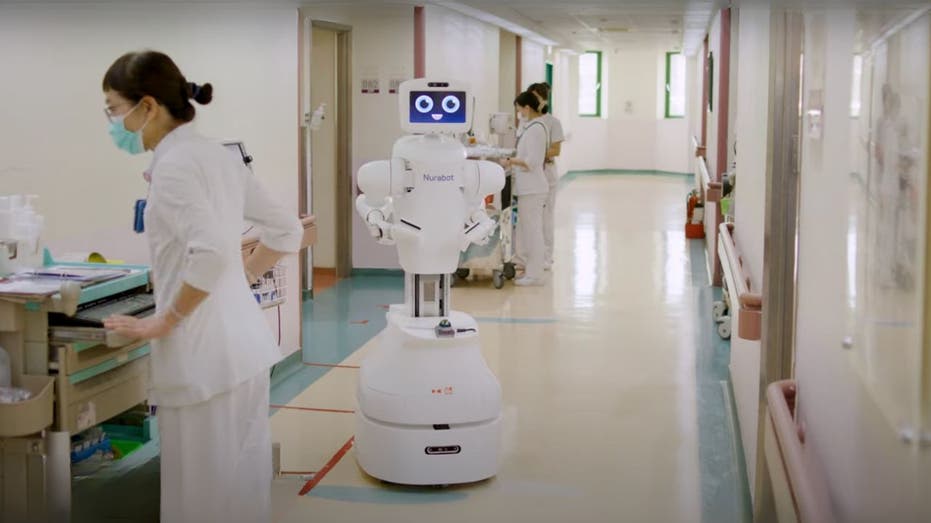
At the forefront of this technological push is Nurabot, a collaborative nursing robot developed through a partnership between Foxconn, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, and powered by Nvidia's advanced AI technology. Nurabot is specifically designed to manage physically strenuous and repetitive tasks, such as delivering medications, transporting medical samples, patrolling wards, and guiding visitors throughout hospital corridors. By taking over these duties, the robot alleviates much of the physical strain that often leads to nurse fatigue and burnout, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex and patient-centered aspects of care.
This digital transformation extends beyond robotics. Foxconn has introduced a comprehensive suite of digital tools built on Nvidia’s platforms, including AI systems that continuously monitor patient vital signs and digital twins—virtual replicas of hospital environments—for planning and staff training. Hospitals utilize data centers to train robust AI models on Nvidia supercomputers and prepare robots virtually before bringing them into real clinical settings. This ensures safety, efficiency, and a smooth integration with existing hospital operations.
One institution leading the charge is Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH), which has created digital twins of its wards and nursing stations as testing grounds for new technologies. As a result, TCVGH and other top Taiwanese hospitals are able to thoroughly train both staff and robots, enhancing their ability to work together seamlessly. According to hospital administrators, such innovations are already boosting staff capacity and allowing nurses to deliver more meaningful care.
On the ground, Nurabot’s presence is transforming day-to-day operations. The robot conducts medicine deliveries, patrols wards, and assists with wayfinding—tasks that previously consumed a significant portion of nurses’ shifts. Foxconn estimates that Nurabot can cut nurse workload by up to 30%. In practice, the robot shuttles wound care kits and educational materials directly to patient bedsides, meaning nurses can avoid multiple trips to supply rooms and spend more time at patients’ sides. Nurabot proves particularly valuable during peak visiting hours and overnight shifts, when staffing numbers are typically stretched thin.
Looking to the future, healthcare workers are optimistic about even more advanced capabilities. There are hopes that upcoming versions of Nurabot will be able to converse with patients in various languages, identify individuals for personalized service, and even assist with physically demanding tasks, such as helping patients sit up or move. In practical terms, this means one nurse—supported by a robot—may be able to accomplish what once required a pair, multiplying the reach and impact of essential healthcare staff.
The integration of AI and robotics in Taiwan’s hospitals represents a significant shift in addressing the looming nursing shortage. Rather than being replaced by machines, nurses are benefiting from a collaborative partnership that allows them to concentrate on the most fulfilling and important parts of their profession. With robots tackling time-consuming errands and routine duties, nurses are left empowered to make a greater difference in the lives of their patients. If this model proves successful, it could become a blueprint for hospitals worldwide seeking to combat staff shortages and improve patient care through innovation.